Google’s trying to make waves with Gemini, its flagship suite of generative AI models, apps and services.
So what is Gemini? How can you use it? And how does it stack up to the competition?
To make it easier to keep up with the latest Gemini developments, we’ve put together this handy guide, which we’ll keep updated as new Gemini models, features and news about Google’s plans for Gemini are released.
What is Gemini?
Gemini is Google’s long-promised, next-gen GenAI model family, developed by Google’s AI research labs DeepMind and Google Research. It comes in three flavors:
- Gemini Ultra, the most performant Gemini model.
- Gemini Pro, a “lite” Gemini model.
- Gemini Nano, a smaller “distilled” model that runs on mobile devices like the Pixel 8 Pro.
All Gemini models were trained to be “natively multimodal” — in other words, able to work with and use more than just words. They were pretrained and fine-tuned on a variety of audio, images and videos, a large set of codebases and text in different languages.
This sets Gemini apart from models such as Google’s own LaMDA, which was trained exclusively on text data. LaMDA can’t understand or generate anything other than text (e.g., essays, email drafts), but that isn’t the case with Gemini models.
What’s the difference between the Gemini apps and Gemini models?
Image Credits: Google
Google, proving once again that it lacks a knack for branding, didn’t make it clear from the outset that Gemini is separate and distinct from the Gemini apps on the web and mobile (formerly Bard). The Gemini apps are simply an interface through which certain Gemini models can be accessed — think of it as a client for Google’s GenAI.
Incidentally, the Gemini apps and models are also totally independent from Imagen 2, Google’s text-to-image model that’s available in some of the company’s dev tools and environments.
What can Gemini do?
Because the Gemini models are multimodal, they can in theory perform a range of multimodal tasks, from transcribing speech to captioning images and videos to generating artwork. Some of these capabilities have reached the product stage yet (more on that later), and Google’s promising all of them — and more — at some point in the not-too-distant future.
Of course, it’s a bit hard to take the company at its word.
Google seriously underdelivered with the original Bard launch. And more recently it ruffled feathers with a video purporting to show Gemini’s capabilities that turned out to have been heavily doctored and was more or less aspirational.
Still, assuming Google is being more or less truthful with its claims, here’s what the different tiers of Gemini will be able to do once they reach their full potential:
Gemini Ultra
Google says that Gemini Ultra — thanks to its multimodality — can be used to help with things like physics homework, solving problems step-by-step on a worksheet and pointing out possible mistakes in already filled-in answers.
Gemini Ultra can also be applied to tasks such as identifying scientific papers relevant to a particular problem, Google says — extracting information from those papers and “updating” a chart from one by generating the formulas necessary to re-create the chart with more recent data.
Gemini Ultra technically supports image generation, as alluded to earlier. But that capability hasn’t made its way into the productized version of the model yet — perhaps because the mechanism is more complex than how apps such as ChatGPT generate images. Rather than feed prompts to an image generator (like DALL-E 3, in ChatGPT’s case), Gemini outputs images “natively,” without an intermediary step.
Gemini Ultra is available as an API through Vertex AI, Google’s fully managed AI developer platform, and AI Studio, Google’s web-based tool for app and platform developers. It also powers the Gemini apps — but not for free. Access to Gemini Ultra through what Google calls Gemini Advanced requires subscribing to the Google One AI Premium Plan, priced at $20 per month.
The AI Premium Plan also connects Gemini to your wider Google Workspace account — think emails in Gmail, documents in Docs, presentations in Sheets and Google Meet recordings. That’s useful for, say, summarizing emails or having Gemini capture notes during a video call.
Gemini Pro
Google says that Gemini Pro is an improvement over LaMDA in its reasoning, planning and understanding capabilities.
An independent study by Carnegie Mellon and BerriAI researchers found that the initial version of Gemini Pro was indeed better than OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 at handling longer and more complex reasoning chains. But the study also found that, like all large language models, this version of Gemini Pro particularly struggled with mathematics problems involving several digits, and users found examples of bad reasoning and obvious mistakes.
Google promised remedies, though — and the first arrived in the form of Gemini 1.5 Pro.
Designed to be a drop-in replacement, Gemini 1.5 Pro is improved in a number of areas compared with its predecessor, perhaps most significantly in the amount of data that it can process. Gemini 1.5 Pro can take in ~700,000 words, or ~30,000 lines of code — 35x the amount Gemini 1.0 Pro can handle. And — the model being multimodal — it’s not limited to text. Gemini 1.5 Pro can analyze up to 11 hours of audio or an hour of video in a variety of different languages, albeit slowly (e.g., searching for a scene in a one-hour video takes 30 seconds to a minute of processing).
Gemini 1.5 Pro entered public preview on Vertex AI in April.
An additional endpoint, Gemini Pro Vision, can process text and imagery — including photos and video — and output text along the lines of OpenAI’s GPT-4 with Vision model.
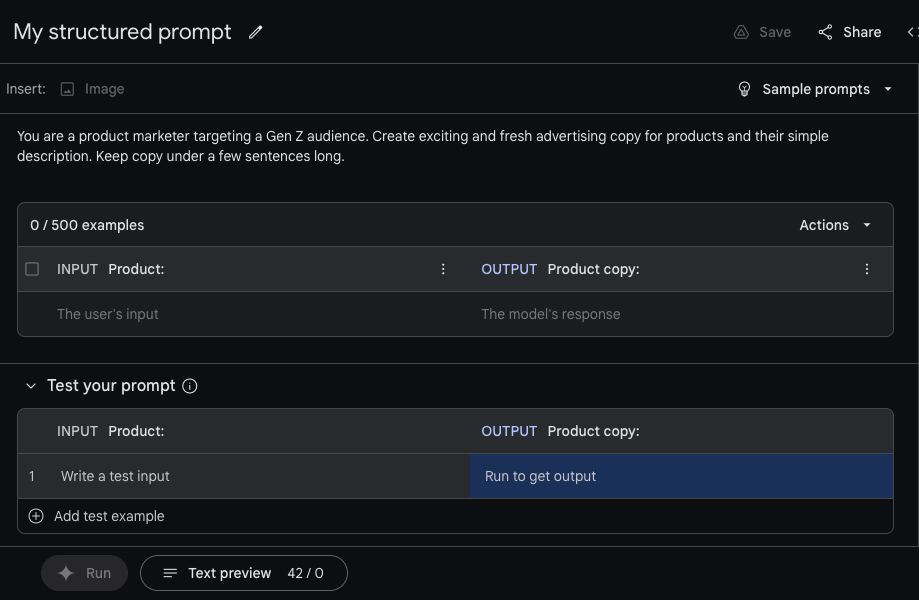
Using Gemini Pro in Vertex AI. Image Credits: Gemini
Within Vertex AI, developers can customize Gemini Pro to specific contexts and use cases using a fine-tuning or “grounding” process. Gemini Pro can also be connected to external, third-party APIs to perform particular actions.
In AI Studio, there’s workflows for creating structured chat prompts using Gemini Pro. Developers have access to both Gemini Pro and the Gemini Pro Vision endpoints, and they can adjust the model temperature to control the output’s creative range and provide examples to give tone and style instructions — and also tune the safety settings.
Gemini Nano
Gemini Nano is a much smaller version of the Gemini Pro and Ultra models, and it’s efficient enough to run directly on (some) phones instead of sending the task to a server somewhere. So far, it powers a couple of features on the Pixel 8 Pro, Pixel 8 and Samsung Galaxy S24, including Summarize in Recorder and Smart Reply in Gboard.
The Recorder app, which lets users push a button to record and transcribe audio, includes a Gemini-powered summary of your recorded conversations, interviews, presentations and other snippets. Users get these summaries even if they don’t have a signal or Wi-Fi connection available — and in a nod to privacy, no data leaves their phone in the process.
Gemini Nano is also in Gboard, Google’s keyboard app. There, it powers a feature called Smart Reply, which helps to suggest the next thing you’ll want to say when having a conversation in a messaging app. The feature initially only works with WhatsApp but will come to more apps over time, Google says.
And in the Google Messages app on supported devices, Nano enables Magic Compose, which can craft messages in styles like “excited,” “formal” and “lyrical.”
Is Gemini better than OpenAI’s GPT-4?
Google has several times touted Gemini’s superiority on benchmarks, claiming that Gemini Ultra exceeds current state-of-the-art results on “30 of the 32 widely used academic benchmarks used in large language model research and development.” The company says that Gemini 1.5 Pro, meanwhile, is more capable at tasks like summarizing content, brainstorming and writing than Gemini Ultra in some scenarios; presumably this will change with the release of the next Ultra model.
But leaving aside the question of whether benchmarks really indicate a better model, the scores Google points to appear to be only marginally better than OpenAI’s corresponding models. And — as mentioned earlier — some early impressions haven’t been great, with users and academics pointing out that the older version of Gemini Pro tends to get basic facts wrong, struggles with translations and gives poor coding suggestions.
How much does Gemini cost?
Gemini 1.5 Pro is free to use in the Gemini apps and, for now, AI Studio and Vertex AI.
Once Gemini 1.5 Pro exits preview in Vertex, however, the model will cost $0.0025 per character while output will cost $0.00005 per character. Vertex customers pay per 1,000 characters (about 140 to 250 words) and, in the case of models like Gemini Pro Vision, per image ($0.0025).
Let’s assume a 500-word article contains 2,000 characters. Summarizing that article with Gemini 1.5 Pro would cost $5. Meanwhile, generating an article of a similar length would cost $0.1.
Ultra pricing has yet to be announced.
Where can you try Gemini?
Gemini Pro
The easiest place to experience Gemini Pro is in the Gemini apps. Pro and Ultra are answering queries in a range of languages.
Gemini Pro and Ultra are also accessible in preview in Vertex AI via an API. The API is free to use “within limits” for the time being and supports certain regions, including Europe, as well as features like chat functionality and filtering.
Elsewhere, Gemini Pro and Ultra can be found in AI Studio. Using the service, developers can iterate prompts and Gemini-based chatbots and then get API keys to use them in their apps — or export the code to a more fully featured IDE.
Code Assist (formerly Duet AI for Developers), Google’s suite of AI-powered assistance tools for code completion and generation, is using Gemini models. Developers can perform “large-scale” changes across codebases, for example updating cross-file dependencies and reviewing large chunks of code.
Google’s brought Gemini models to its dev tools for Chrome and Firebase mobile dev platform, and its database creation and management tools. And it’s launched new security products underpinned by Gemini, like Gemini in Threat Intelligence, a component of Google’s Mandiant cybersecurity platform that can analyze large portions of potentially malicious code and let users perform natural language searches for ongoing threats or indicators of compromise.
